Key Takeaways
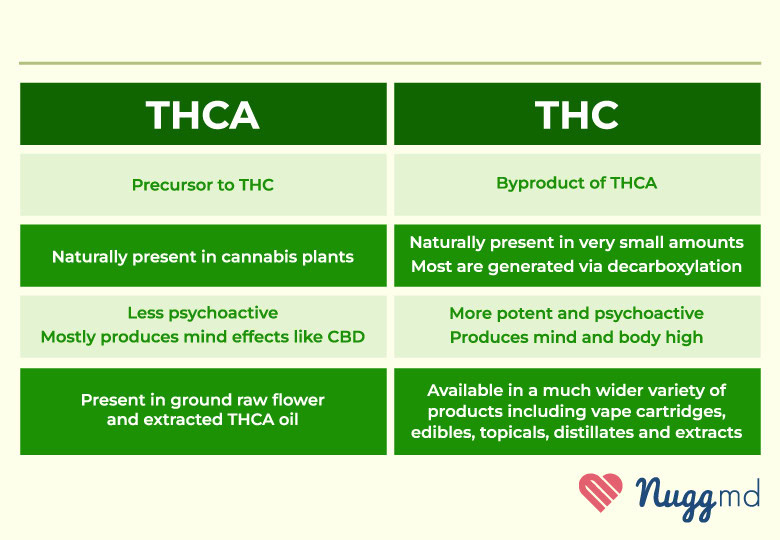
- THCA is a non-intoxicating precursor cannabinoid to THC.
- THCA converts to THC when cannabis flower is heated, a process called decarboxylation.
- Both THCA and THC offer therapeutic effects, with THC producing intoxicating effects.
Cannabis strains contain hundreds of compounds. Headlined by the most prevalent of them all, the cannabinoid THC. There’s no doubt that THC plays a massive role in the cannabis experience. But, the multitude of other compounds also play their part, including THCA. So, when comparing THCA vs THC, what do you need to know?
What is THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary intoxicating compound found in cannabis strains, otherwise known as cultivars. The most prevalent compound found in most strains, THC binds to the body’s cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system. This system is known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
When THC binds to the ECS, various effects can be produced, including euphoria, relaxation, and altered sensory perception. Likewise, it may provide other benefits, including nausea relief, appetite stimulation, and pain relief, both physical and mental.
What is THCA?

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is the non-intoxicating precursor to THC.1 Instead of being rich in THC, raw cannabis buds are actually rich in THCA. That’s why if someone were to eat raw flower, they wouldn’t feel the intoxicating effects like they would from an infused edible.
Before cannabis can create its well-known intoxicating effect, the plant must undergo a process called decarboxylation. This process changes the plant’s chemical makeup, converting THCA into the intoxicating cannabinoid most associated with the plant.
The conversion process is achieved using several methods, including exposure to sunlight. However, heating is the primary method utilized. Those making edibles or infused oils will use several methods, including old school, heating in the oven, or more modern, cannabis specific decarbing tools. But, for anyone smoking a bowl, blunt, joint, spliff, or other flower option, the conversion occurs when the flower is set on fire.
Is a THCA high the same as THC?
No. That’s because THCA doesn’t produce an intoxicating high at all. To produce intoxicating effects, THCA flower needs to be heated, converting the compound from THCA to THC. Without fire or heat, THCA will not convert and will not produce intoxicating “high” effects.
Some may overlook THCA and other non-intoxicating cannabinoids. That, however, is likely a mistake considering the other benefits minor cannabinoids like THCA possess.
Effects of THCA

THCA has been reported to have the potential for various therapeutic effects. Researchers have identified several possible benefits, including:
- Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties beneficial in neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's.2
- Antioxidant activity, helping combat free radicals in the body.3
- Potential memory improvement.4
- Decreased amyloid-beta and tau pathology in Alzheimer's models.
- Neuroprotective effects, potentially valuable in treating conditions like Huntington's disease.5
THCA vs THC: Which is Stronger?
In cannabis, “stronger” typically refers to how high a person might feel, or how strong they feel the effects of the strain. If that’s the criteria, THC wins due to its intoxicating effects, a rather rare trait in most cannabis compounds.
But, a more effective question might be, what do THC and THCA have to offer? Asking something like this helps understand that “strength” isn’t as much a factor as the effects produced. Consider each compound:
- THC: An intoxicating compound, THC binds to CB1 receptors, producing various effects, ranging from feelings of euphoria to appetite stimulation, nausea relief, and pain reduction. If consumed in excessive amounts, THC may become adverse, potentially causing non-deadly side effects like anxiety, paranoia, and dizziness in some consumers.6
- THCA: A non-intoxicating compound, THCA shows limited affinity to CB1 and CB2 receptors, unlike THC. Still, it has shown some therapeutic potential, including neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant benefits.
Legality of THCA
THCA and most other cannabis compounds operate in a unique legal space, where availability differs immensely by state rules. The confusion and state-by-state law structure is largely due to a loophole in the 2018 Farm Bill.
Under the bill, cannabis plants with less than 0.3% delta-9 THC are considered hemp. That was the intent of the 2018 bill. However, in an attempt to make hemp legal at the federal level, the wording of the law allowed just about every plant compound to be sold. This is why many states with restricted cannabis markets may still sell THCA and other cannabinoid-centric products at a variety of non-dispensary locations, including gas stations.
In response, numerous states have rolled back laws on the state level, with others considering their options at the time this article was published.
Is that why THCA is being banned in the U.S.?
Bans are taking place against THCA in the states, but not on the federal level at this time. While THCA isn't banned federally, states are attempting to regulate or prohibit the cannabinoid due to its ability to convert to THC. In some states, it’s also believed that the bans are being instituted to help the legalized market, including THC retailers and producers.
THCA Flower vs. THC Flower
While both appear beneficial for a variety of consumers, THCA and THC are far from the same experience. However, thanks to decarboxylation, the two experiences overlap significantly.
Cannabis is naturally high in THCA prior to decarboxylation. By selling flower as THCA, retailers in even the most restrictive cannabis states, such as North Carolina, can sell products that are destined to become THC. As such, many states have pushed back. At the same time, some less-than-reputable retailers have begun selling THCA flower, even gas stations and convenience stores.
At the end of the day, all cannabis flower contains various amounts of THCA until it's heated or set on fire. No matter where or what product type they’re about to buy, consumers should check that the flower is of good quality. Look for the certificate of authenticity (COA) on the product packaging or website to confirm its contents and lab results.
References
- Skell JM, Kahn M, Foxman BM. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid A, the precursor to Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Acta Crystallographica Section C Structural Chemistry. 2021;77(2):84-89. doi:https://doi.org/10.1107/s2053229621000280 ↩︎
- Moreno-Sanz G. Can You Pass the Acid Test? Critical Review and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid A. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. 2016;1(1):124-130. doi:https://doi.org/10.1089/can.2016.0008 ↩︎
- Dawidowicz AL, Olszowy-Tomczyk M, Typek R. CBG, CBD, Δ9-THC, CBN, CBGA, CBDA and Δ9-THCA as antioxidant agents and their intervention abilities in antioxidant action. Fitoterapia. 2021;152:104915. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2021.104915 ↩︎
- Kim J, Choi P, Park Y-T, Kim T, Ham J, Kim J-C. The Cannabinoids, CBDA and THCA, Rescue Memory Deficits and Reduce Amyloid-Beta and Tau Pathology in an Alzheimer’s Disease-like Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(7):6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24076827 ↩︎
- Nadal X, Del Río C, Casano S, et al. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(23):4263-4276. doi:10.1111/bph.14019 ↩︎
- Ng T, Gupta V. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563174/ ↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




