In This Article
- What is THCA?
- Is THCA Natural or Synthetic?
- What Does THCA Do?
- Is THCA Psychoactive?
- THC vs THCA: What’s the Difference?
- What are the Benefits of THCA?
- How Powerful is THCA?
- What are the Cons and Side Effects of THCA?
- How to Use THCA
- How Do You Turn THCA Into THC?
- THCA Products
- Is THCA Legal in Every State?
- THCA vs CBD
- THCA vs Delta 8
- THCA vs THCV
- Is THCA legal?
- What are THCA Diamonds?
- What is a Good THCA Percentage?
- References
The cannabis plant produces over 100 cannabinoids. The general public has become familiar with the major ones, like THC and CBD, but then there are the lesser-known, minor cannabinoids, including the likes of CBN, THCV, CBG, CBDA, and THCA.1
THCA is the acidic form of THC, and while THC is what causes the intoxicating effects of cannabis, there’s actually very little of it found in the cannabis plant. The raw plant material is rich in THCA, which converts to THC once the heat is applied. This process is called decarboxylation.2
While THC may be the star cannabinoid with seemingly endless uses for both medicinal and recreational consumers, THCA has its own list of benefits that make it well worth noting.
What is THCA?
Cannabinoids are produced by the plant as a defense mechanism and are affected by the environment in which it grows. THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is one cannabinoid found naturally in the cannabis plant in generous amounts. It’s a natural and necessary key to many of the plant’s potential therapeutic benefits.
Despite its abundance in raw cannabis plant material, much less of it is actually consumed.3 That’s because, to feel the intoxicating effects of cannabis, THCA must be converted to THC, which requires heat. This usually happens in joints, bongs, dabs, and bowls when a flame or heat is applied to the dry flower or cannabis concentrate. But for edibles, tinctures, and topicals, individuals must use decarboxylation methods to chemically convert THCA into intoxicating THC.
CBD is another cannabinoid that has to undergo the same process because CBDA is the cannabinoid that the plant more readily produces. The difference between these two is how CBDA interacts with the body, which may make it a more suitable cannabinoid for pain management. Similarly, THCA and THC have a few prominent differences beyond their chemical structure, including how they feel when consumed.
Is THCA Natural or Synthetic?
THCA is a natural cannabinoid. It’s produced in raw cannabis as the precursor to THC and forms naturally as the plant matures. Unlike synthetic cannabinoids, THCA hasn’t been lab-created or altered to mimic THC—it’s already part of the plant’s chemistry.
What Does THCA Do?
THCA itself doesn’t get you high, but it may offer potential benefits like reducing inflammation, nausea, or seizures. Some research also suggests the cannabinoid may offer neuroprotective properties. While studies are still early, some cannabis consumers use THCA-rich products in pursuit of therapeutic benefits.
Is THCA Psychoactive?

Since THC can produce psychoactive and intoxicating effects, many people wonder if THCA is also psychoactive. THCA is a psychoactive compound, but THCA will not induce any intoxicating effects unless it is decarboxylated. THCA does not bind to the CB1 receptors like THC,4 but it does have a range of therapeutic applications at other receptors within the brain, like the PPARγ channel.5
THC vs THCA: What’s the Difference?
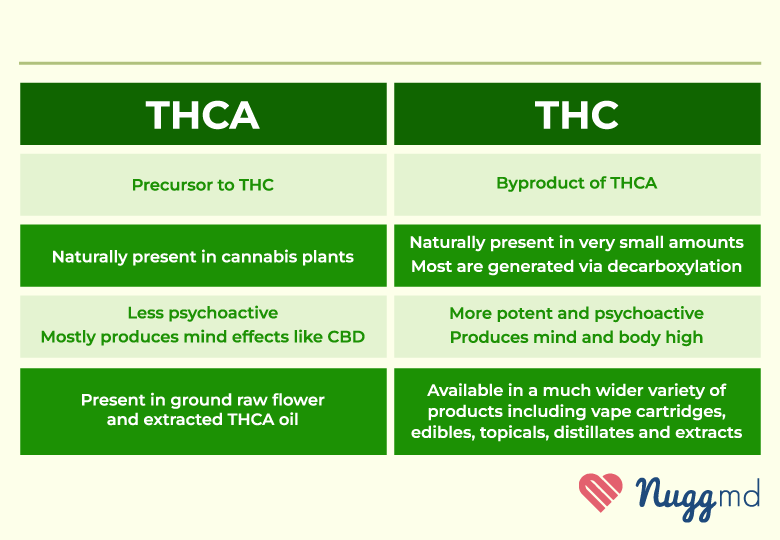
THC and THCA are closely related, with THCA being the precursor to THC. THCA is non-intoxicating until it’s heated through smoking, vaping, or cooking. Once it undergoes decarboxylation, it becomes delta-9 THC, the form that produces intoxicating effects. Consuming THCA will not produce any intoxicating effects, unlike THC.
THCA is readily available in raw cannabis but has started to be isolated and infused into products like capsules and tinctures. THC is easier to find in states where adult-use or medical cannabis is available in various products.
What are the Benefits of THCA?

THCA has a wide range of therapeutic effects, only without the intoxicating feelings of THC. This has made it a highly desirable treatment option for many medical cannabis patients. In fact, it has been studied for its neuroprotective properties, which researchers say may be worth considering for related neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions.5
Additionally, researchers did a study on rats and found that THCA may help treat symptoms related to obesity, like metabolic syndrome and inflammation. Some research even suggests that THCA may help reduce the size of tumors without causing any adverse side effects, though further research is needed. And THCA has shown some potential to be even more effective than THC in reducing symptoms of nausea and vomiting.6
A study from 2021 done in mice found that THCA mediates anti-arthritis activity at the CB1 and PPARγ receptors.7
Most of these studies were done on rats, and further studies are needed to confirm THCA’s benefits are also replicable in human patients.
How Powerful is THCA?
THCA itself won’t get you high, but once it converts into THC it can be just as powerful as any other high-THC product. The potency depends on how much THCA is present and how it’s consumed. When decarboxylated (heated), THCA converts to traditional delta-9 THC and carries the same potential for psychoactive effects.
What are the Cons and Side Effects of THCA?
The primary drawback of THCA appears to be that it is limited to select products on dispensary shelves and raw cannabis material.
No research or reports of THCA causing any intoxicating effects exist. This doesn’t mean that there may not be any. It just may be that the adverse side effects are so minimal that it would take excessive amounts of THCA to induce any.
How to Use THCA
THCA can be found in the cannabis plant. It may also be extracted and isolated into products like diamonds, tinctures, capsules, and THCA powder.
Even though THCA doesn’t cause any intoxicating effects, it’s best to exercise caution as you consume it, especially if it’s your first time. Tinctures and capsules should be taken as directed, starting off with the lowest dose you’re comfortable with.
Using raw flower material may be one of the more prominent ways to consume THCA as it may be the most rich in other cannabinoids and terpenes. Many people add cannabis leaves into smoothies, juices, and other foods as a general supplement-style ingredient. The difference between consuming cannabis raw and using it for edibles is that, to get the benefits of THCA, you’ll skip the decarboxylation process. So, if you're looking to consume raw cannabis for THCA, don't decarb before using it in your desired infusion.
How Do You Turn THCA Into THC?
To turn THCA into THC, you’ll need to decarb the material. This is the process of applying heat to the raw cannabis material.
THCA Products

THCA products are available for purchase in high-THC cannabis-derived and high-CBD hemp-derived options. Often they are found in tinctures, diamonds, and infused pre-rolls like the following:
- Rosette Tinctures has a line of tinctures formulated for different needs – including a THCA and CBDA dominant option.
- Papa and Barkley is a well-known cannabis wellness brand. Their tinctures, one of which is a high THCA version, are long-lasting and effective.
- Bear Labs Bud Booster THCA Diamonds are so good they sell out quickly. This may be a good option for those looking for higher potency.
- Grizzly Peak Infused Preroll Joints are convenient and potent. Their Indica Bone THCA diamonds are great for high-tolerance users.
Is THCA Legal in Every State?
Some states have moved to ban THCA products, especially where laws prohibit anything that becomes intoxicating when heated. As of 2024, states restricting or banning THCA include Arkansas, Hawaii, Minnesota, North Dakota, and Oregon. Laws are shifting rapidly, so check your state’s current cannabis laws before purchasing.
THCA vs CBD
THCA is similar to CBD, since they are both cannabinoids that do not induce intoxicating effects. They also have many potential medicinal applications for treating different ailments.
CBD is a byproduct of CBDA that, more often than not, needs to be decarbed before getting extracted. CBD has been well studied for its ability to help aid in symptoms related to pain, anxiety, and depression.8 It has further benefits that may be helpful in the treatment of conditions like seizures and liver conditions.9 Professionals also warn consumers of the adverse side effects of consuming CBD that include drowsiness, fatigue, and diarrhea
THCA vs Delta 8

Like THC, delta-8 can come from THCA-rich cannabis. However, even after decarboxylation, it still only appears in miniscule quantities. So it tends to be chemically created from CBD isolate instead. Because of this, it has become increasingly popular as the Farm Bill has allowed hemp products to be used and produced, including hemp-derived minor cannabinoids that substitute for lack of delta-9 (THC) in places where adult-use or medical cannabis remains illegal.
While THCA and delta-8 are both minor cannabinoids that have only recently garnered real attention, THCA does not cause intoxicating effects, while delta-8 does. Delta-8 has benefits that mimic THC with lower potency, including relaxation, euphoria, and pain management.10 THCA may also be helpful in pain-related symptoms.
THCA vs THCV
THCV is a minor cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Like THCA, it is not intoxicating and has been studied for its ability to help aid in obesity-related issues. One study found that THCV may be helpful for neuroprotection and appetite suppression. These findings have played a part in THCV getting the nickname “diet weed,” but some studies say that THCV isn’t necessarily reducing appetite, but instead playing a role in regulating glucose and insulin levels.11
THCV's ability to help with weight-related issues may also be its largest drawback, as not all consumers are looking for those effects. When deciding which cannabinoid may be better for treating obesity-related symptoms, choosing between THCA and THCV is a personal decision best discussed with your doctor.

Is THCA legal?
THCA is federally legal under the 2018 Farm Bill as long as it's derived from hemp containing less than 0.3% delta-9 THC. However, because THCA converts to THC when heated, some states have moved to restrict or ban it. Some may view it as a loophole to access THC-rich products. States like New Hampshire and West Virginia have banned THCA outright. Others have imposed stricter regulations.
What are THCA Diamonds?
THCA diamonds are a highly potent isolated THCA concentrate that takes the form of tiny crystals or diamonds. They can be consumed independently through dabbing or added to joints or bowls to enhance their potency and flavor (though both of these methods will convert them into THC).
What is a Good THCA Percentage?
There is no scientific data to support what a ‘good’ THCA percentage is. That said, some connoisseurs note that the average level is anywhere between 15 -25% THCA.
References
1. Walsh KB, McKinney AE, Holmes AE. Minor Cannabinoids: Biosynthesis, Molecular Pharmacology and Potential Therapeutic Uses. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2021;12. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.777804
2. Filer CN. Acidic Cannabinoid Decarboxylation. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. 2021;7(3). doi:https://doi.org/10.1089/can.2021.0072
3. Coogan, Thomas A. “Analysis of the Cannabinoid Content of Strains Available in the New Jersey Medicinal Marijuana Program.” Journal of Cannabis Research, vol. 1, no. 1, Dec. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-019-0011-z. Accessed 27 Mar. 2020.
4. Raïch I, Rivas-Santisteban R, Lillo A, et al. Similarities and differences upon binding of naturally occurring Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-derivatives to cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacological Research. 2021;174:105970-105970. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105970
5. Nadal X, Del Río C, Casano S, et al. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(23):4263-4276. doi:10.1111/bph.14019
6. Moreno-Sanz G. Can You Pass the Acid Test? Critical Review and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid A. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. 2016;1(1):124-130. doi:https://doi.org/10.1089/can.2016.0008
7. Palomares B, Garrido-Rodríguez M, Gonzalo-Consuegra C, et al. Δ 9 ‐Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid alleviates collagen‐induced arthritis: Role of PPARγ and CB 1 receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2020;177(17):4034-4054. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15155
8. Rapin L, Gamaoun R, El Hage C, Arboleda MF, Prosk E. Cannabidiol use and effectiveness: real-world evidence from a Canadian medical cannabis clinic. Journal of Cannabis Research. 2021;3(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00078-w
9. Meissner H, Cascella M. Cannabidiol (CBD). PubMed. Published 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556048
10. Kruger JS, Kruger DJ. Delta-8-THC: Delta-9-THC’s nicer younger sibling? Journal of Cannabis Research. 2022;4(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00115-8
11. Abioye A, Ayodele O, Marinkovic A, Patidar R, Akinwekomi A, Sanyaolu A. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV): a commentary on potential therapeutic benefit for the management of obesity and diabetes. Journal of Cannabis Research. 2020;2(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-020-0016-7
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




