In This Article
- What is Transplanting?
- Why Do Cannabis Transplanting?
- Avoid Root Binding
- Separate Male and Female Plants
- Adjust to a New Environment
- Scale Up Your Grow
- Micro-Growing
- Changing the Growing Environments
- When Should You Transplant Cannabis?
- How Much Space Should There Be?
- How to Transplant Cannabis
- Step 1: Choose the Right Container
- Step 2: Prepare the New Container
- Step 3: Carefully Remove the Plant
- Step 4: Transplant
- Step 5: Water the Plant
- Step 6: Provide Proper Care
- How to Avoid Transplant Shock
- Why Not Just Use the Biggest Pot From the Start?
- Do Autoflowering Plants Need to Be Transplanted?
- What Are the Signs of a Rootbound Plant?
- Should I Water Right After Transplanting?
- Does My Plant Need Light After a Transplant?
- References
Key Takeaways
- Transplanting helps cannabis thrive by giving roots more room to grow.
- The best time to transplant is during the vegetative stage, or about 2-4 weeks after germination.
- Avoid transplant shock by being gentle with roots and giving your plant time to adjust.
Growing cannabis isn’t just about water, light, and patience. It’s also about knowing when to make key moves, and cannabis transplanting is one of the biggest. Done right, it sets the stage for a strong root system and a solid harvest. Done wrong, it can stress your plant and slow things down.
Whether you’re new to growing or just brushing up, this guide covers when and how to transplant cannabis, plus how to avoid common pitfalls like transplant shock.
What is Transplanting?
Transplanting means moving your cannabis plant from one container or location to another. This might sound simple, but the timing and method matter more than one might think. Growers might transplant for several reasons:
- The plant starts to outgrow its current container, or reaches its vegetative stage.
- It's time to change its environment entirely (like moving from indoors to outdoors).
- Transplanting promotes faster, healthier growth, enables better nutrient uptake, and helps prevent root binding.
Think of transplanting like upgrading your plant’s home. It gives roots more space, helps avoid nutrient lockout, and keeps your plant on track for healthy growth.
Why Do Cannabis Transplanting?

Transplanting is as much about strategy as it is about giving your plant a new space to keep growing.
Avoid Root Binding
When roots run out of room, they start circling the pot and tangling up. This can stunt growth or even lead to root rot. Transplanting into a bigger container lets those roots stretch out and breathe.
Separate Male and Female Plants
Once your plants start to show their sex (usually in early veg), separating males from females helps prevent accidental pollination. That’s key if you're aiming for high-quality, seedless buds.
Adjust to a New Environment
Some growers start plants indoors and move them outside later. Some might shift between soil and hydro setups. Transplanting makes those transitions smoother.
Scale Up Your Grow
If you started with a micro-grow, transplanting lets you upgrade without starting from scratch.
Transplanting the plant into a larger container or a raised bed can give the roots more space to expand, increasing the plant’s overall health and maximizing your yield.
Micro-Growing
Another reason to transplant cannabis is to go from a micro-grow setup to a larger space. Micro-grows are small-scale growing methods within a small area. As the plant grows, it may become necessary to transplant it to a bigger space.
Changing the Growing Environments
Cultivators often transplant cannabis plants to change the growing environment. For example, a grower may start their plants indoors and transplant them outside when the weather is appropriate. Or they may be transplanted from a hydroponics system to soil.
Ultimately, cannabis transplanting can be a beneficial practice for growers as it can help improve the plant’s health, increase yield, and better control the plant's sex.
When Should You Transplant Cannabis?

The sweet spot for transplanting is during the vegetative stage, usually between 2 and 4 weeks after germination. At this point, your plant is focused on growing leaves and stems, not flowering, so it’s less vulnerable to stress.
Think it might be time to transplant? Watch for these signs:
- Leaves start overlapping or crowding each other.
- Roots poke out of the drainage holes.
- The plant seems too tall for its pot.
- Growth slows down, or leaves begin yellowing.
If you're growing in soil, you might be able to transplant more often than if you’re in hydroponics, where roots are more sensitive to disturbance.
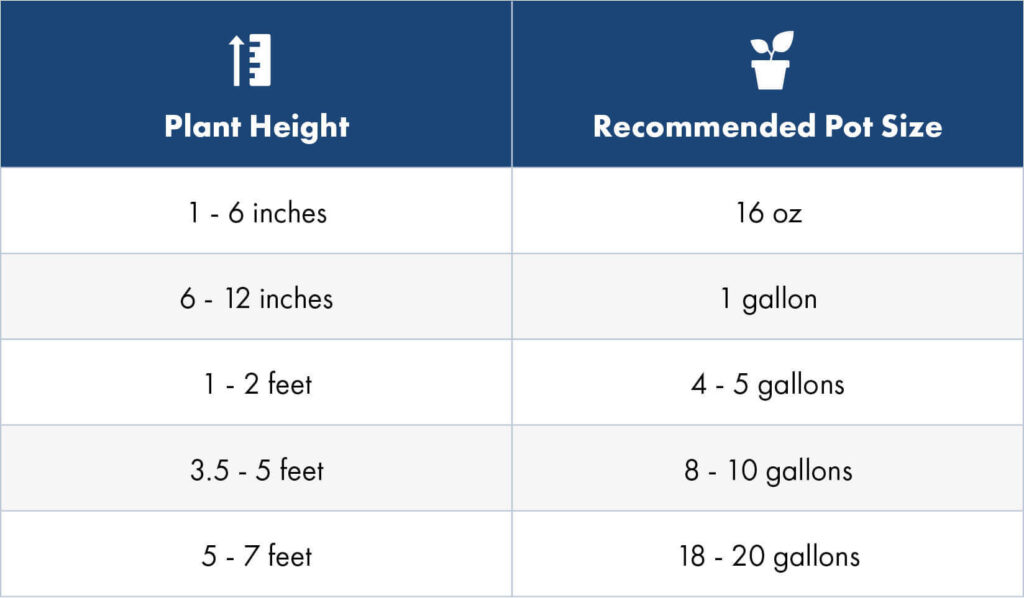
How Much Space Should There Be?
Before transplanting your cannabis plants, consider the following guidelines to find the right pot size for your plant’s height.
How to Transplant Cannabis
Here’s a simple step-by-step process you can follow to transplant your cannabis plant.
Step 1: Choose the Right Container
Pick a container that’s big enough for your plant to grow into, not just for now, but for the next several weeks. A 5-gallon pot is a good standard for many growers. Make sure it has proper drainage.
Step 2: Prepare the New Container
Fill it with a well-aerated, high-quality growing medium. If you’re using soil, make sure it’s moist, not soggy. This makes it easier for the plant to settle in.
Step 3: Carefully Remove the Plant
Gently tip the old container upside down and tap the bottom until the plant slides out. If roots are tightly packed, use your fingers to gently loosen them. Be careful not to break or tear anything.
Step 4: Transplant
Place the plant in its new pot at the same depth as before. Backfill with soil and gently press around the base to stabilize the stem.
Step 5: Water the Plant
Water until it drains from the bottom. This helps the roots settle and reduces the risk of air pockets in the soil.
Step 6: Provide Proper Care
You’ve successfully transplanted your cannabis plant. Now, you’ll want to check in daily for signs of stress, like drooping or yellowing leaves. Keep lighting, nutrients, and water consistent as the plant adjusts. You can resume a regular feeding and care schedule once your plant has time to adapt and recover.
Finally, monitor root development. If necessary, transplant the plant again if it outgrows this new container.
How to Avoid Transplant Shock

Transplant shock happens when the roots are damaged or the plant has a hard time adjusting. Here's how to avoid it:
- Be gentle with roots. Try not to tear or crush them.
- Don’t overwater. Soil should be damp, not soaked.
- Skip the fertilizer (at first). Wait a few days before feeding again.
- Keep the environment stable. Sudden changes in temp, light, or humidity can add to the stress.
- Use beneficial microbes. Products like mycorrhizae can support root recovery.1
Why Not Just Use the Biggest Pot From the Start?
While it might seem easier to start with a large container, cannabis roots need to grow into their space. A too-big pot can make it harder for roots to access water evenly and may lead to overwatering or slower growth.
Do Autoflowering Plants Need to Be Transplanted?
Autoflowers grow fast and don’t always bounce back well from stress. If you do transplant them, aim to do it early, ideally before they hit the flowering stage. Some growers skip transplanting entirely and start them in their final pot.
What Are the Signs of a Rootbound Plant?
A rootbound plant might look droopy, grow slower than expected, or have roots poking out of the drainage holes. If you remove it from the pot and see roots circling the base, it’s time to upgrade.
Should I Water Right After Transplanting?
Yes. Water thoroughly after transplanting to help settle the soil and support root recovery. Just avoid overdoing it—soggy soil can lead to root issues.
Does My Plant Need Light After a Transplant?
Absolutely. Light helps the plant bounce back and keep growing. Stick to your normal lighting schedule, and avoid making major changes to your setup during this adjustment period.
References
- Ahmed B, Hijri M. Potential impacts of soil microbiota manipulation on secondary metabolites production in cannabis. Journal of Cannabis Research. 2021;3(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00082-0 ↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




