Delta-8 THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is a compound found in cannabis that is one double-bond away from delta-9 THC (the “THC” responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis, and the one most people are referring to when discussing cannabis). Delta-8 THC gained notoriety in states without legal cannabis when it became known as a loophole for consumers who wanted the “high” that cannabis offers, but didn’t have access to the banned delta-9 THC.
Delta-8 THC goes through a similar metabolic process to delta-9 THC, but it has less affinity for the CB1 receptor when compared to delta-9 THC; thus, it is suspected to produce less pronounced psychoactive effects. One significant difference between delta-9 THC and delta-8 THC is that the latter is more stable (it has a longer shelf life and does not oxidize).
Research on delta-8 THC is still minimal. Many industry professionals advise caution when using delta-8 THC from the unregulated market since it is synthetically produced from hemp-based CBD. Numerous states have begun regulating delta-8 THC in much the same way as the better-known delta-9 THC, while others have banned its sale until sufficient studies can be conducted regarding the product’s effects on consumers.
How Do Cannabinoids Work?
Cannabinoids are found within the resinous trichomes of the cannabis plant. Trichomes are found mainly on female cannabis plants and are abundant on the bracts (where flowering buds develop). Trichomes are also present on the leaves in smaller amounts and can even be found on the seeds.
The cannabinoid THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) accumulates in the glands of capitate-stalked and more abundantly in the capitate sessile trichomes. So how do you get from THCA to delta-8 THC? These cannabinoids are synthesized through synapses in the plant, with THCA synthase producing THCA. From THCA, you get delta-9 THC, which can further degrade to delta-8 THC and CBN. The most abundant cannabinoids produced by the cannabis species are delta-9 THC and CBD, depending on if the plant is of the “hemp” or “marijuana” variety (2).
Since the 1940s, over 100 phytocannabinoids have been discovered. These cannabinoids interact with endocannabinoid receptors throughout the body to modulate your endocannabinoid system. Your body naturally produces endocannabinoids 2-AG and anandamide that interact with receptors throughout your body. When these endocannabinoids are dysregulated, phytocannabinoids – like those found in cannabis – may help boost or supplement these natural endocannabinoid levels. These receptor interactions produce the varying effects of individual and paired cannabinoids.
The cannabinoids found in cannabis are considered secondary metabolites, meaning they have no primary role in the development of the plant. Researchers theorize that cannabinoids are produced as a defense mechanism for the plant, to protect against pests and diseases. It is even suggested that the production of cannabinoids may function as a sunscreen that absorbs harmful UV-B rays (5).
How Does Delta-8 THC Affect the Body?
Delta-8 THC and delta-9 THC both follow the same metabolic pathway, and their chemical behavior is very similar as they are close isomers. Delta-8 THC binds to the CB1 and CB2 receptors, but it has a lower binding affinity than delta-9 THC. Research indicates the potential of delta-8 THC to block the HT3 receptor, which may play a role in its anti-emetic properties (1).
Like all other cannabinoids, delta-8 THC targets several receptors within the body. However, very little research has been conducted on the specific bioactivity of delta-8 THC. Some animal research has suggested it may produce similar benefits as delta-9 THC, but few clinical trials have been completed.
What to Expect When Consuming Delta-8 THC
For delta-8 THC, individuals report feelings of relaxation, pain relief, and euphoria. Compared to delta-9 THC, users state that delta-8 THC is less intense and does not last as long (4). Like other cannabinoids, the effects of delta-8 THC are dependent on an individual’s metabolism, tolerance, diet, and overall body chemistry. Various methods of use for delta-8 THC also produce different responses in individuals and are dose-dependent. Everyone has a unique endocannabinoid system. Thus, there is no universal answer for how delta-8 THC may affect you.
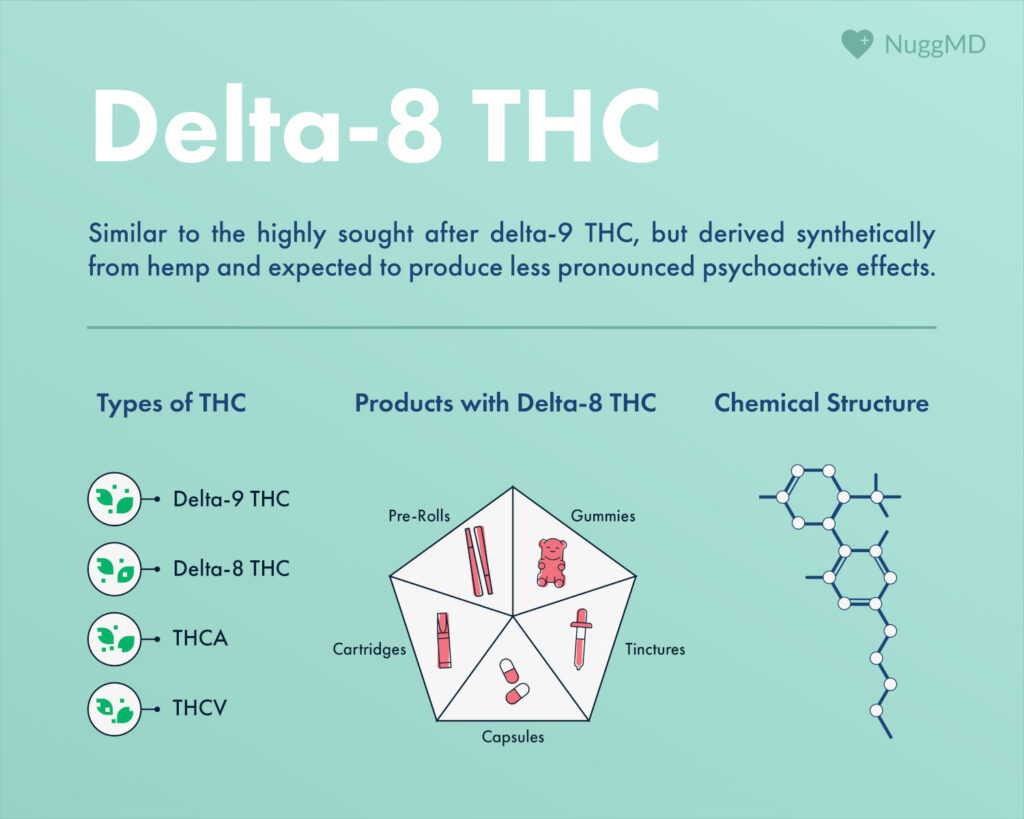
Different Types of THC
- Delta-9 THC. This cannabinoid is the most known phytocannabinoid and the psychoactive compound that people typically refer to when talking about THC.
- Delta-8 THC. Delta-8 THC is an isomer of delta-9 THC and is suggested to produce a milder high while providing similar potential benefits. It is made by converting CBD extracted from hemp and has grown in popularity since 2020.
- Delta-10 THC. Another isomer of delta-9 THC, delta-10 THC, is not produced in significant amounts within the cannabis plant. Like delta-8 THC, it requires converting other cannabinoids such as CBD.
- THCA. THCA is the main cannabinoid produced in the “drug” variety of the cannabis plant. When heated, THCA converts to its psychotropic counterpart delta-9 THC. It will also slowly degrade over time to delta-9 THC if improperly stored. THCA potentially has a lower binding affinity for the CB1 and CB2 receptors but is active at several TRP channels and PPARγ pathways (8, 9).
- THCV. THCV is a nonintoxicating minor cannabinoid. Research suggests that it may increase energy, promote weight loss, and suppress appetite. Early research also demonstrates it may benefit patients with diabetes (10). This cannabinoid is not usually produced in high amounts across most cultivars, but has been seen in strains like Durban Poison and GSC. Doug’s Varin is a cultivar bred explicitly for high THCV production.
History of Delta-8 THC

Raphael Mechoulam was the first to isolate THC and its isomers from the cannabis plant. In 1966 he patented the chemical conversion process to make delta-8 THC from CBD. However, Roger Adams was the first to report the conversion of CBD using acidic solvents in 1940 (3, 4).
Delta-8 THC rose in popularity due to the ease of access to an excess amount of hemp CBD biomass, and a corresponding lack of access to delta-9 THC products considered illegal in some states. Producers figured out that they could use a loophole in the farm bill to sell delta-8 THC. Because the 2018 Farm Bill states that Cannabis plants containing less than 0.3 delta-9 THC and their derived products were descheduled, companies took this as a green light to synthesize other cannabinoids from hemp-derived CBD. In addition to delta-8 THC, companies synthesize CBN, delta-10 THC, hexahydrocannabinol, and more (3). Many states, including recreationally legal states, have taken steps to ban the sale of delta-8 THC products due to a lack of regulation surrounding safety.
Reported Benefits of Delta-8 THC
Research on delta-8 THC benefits is minimal. A limited study from 1995 demonstrates that delta-8 THC may potentially treat nausea in pediatric patients with chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). This study concluded that delta-8 THC at higher doses than delta-9 THC was more tolerable and stopped the CINV (1, 3). However, the sample consisted of only 8 pediatric cancer patients, and more extensive research is needed.
Users have reported that delta-8 THC helps with anxiety, stress, depression, and chronic pain, much like delta-9 THC seems to (7). However, these user reports are anecdotal and are not backed up by clinical evidence. Some animal studies suggest that delta-8 THC may increase appetite and may help with amotivational syndrome.
Risks & Side-Effects of Delta-8 THC
Research on delta-8 THC and its potential long-term risks is limited, and almost 20 states have taken some action to restrict or ban the sale of delta-8 THC. The delta-8 THC sold on the market is synthetically produced from CBD extract. Due to the lack of regulation around how delta-8 THC is produced, chemists in cannabis have voiced their concerns about its safety, stating many of these products have misguided labeling and faulty test reports (3).
Some potential risks or side-effects of consuming delta-8 THC include:
- Sedation
- Throat irritation (if smoking or vaping)
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Dizziness
- Rapid heart rate
- Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD)
Common Ways to Consume Delta-8 THC
The most popular product for delta-8 THC are edibles, with cartridges and dabs a close second. Tinctures with delta-8 THC are the third most popular product. Delta-8 THC products can also be found in flower form that can be smoked or vaped. Some consumers spray delta-8 THC distillate or isolate onto hemp flowers. Other delta-8 THC products include topicals, capsules, and suppositories (6).
Because the delta-8 THC sold on the market is produced synthetically and has not been extensively studied, we recommend sticking with delta-9 THC, which is found naturally in the cannabis plant.
References
- Abrahamov A, Abrahamov A, Mechoulam R. An efficient new cannabinoid antiemetic in pediatric oncology. Life Sciences. 1995;56(23-24):2097-2102. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(95)00194-b
- Andre CM, Hausman J-F, Guerriero G. Cannabis sativa: The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules. Frontiers in Plant Science. 2016;7. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00019
- Babalonis S, Raup-Konsavage, WM, Akpunonu, PD, Balla, A, and Vrana, KE. Δ8-THC: Legal Status, Widespread Availability, and Safety Concerns. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. Oct 2021; 6(5): 362-365. http://doi.org.proxy-hs.researchport.umd.edu/10.1089/
- Golombek P, Müller M, Barthlott I, Sproll C, Lachenmeier DW. Conversion of Cannabidiol (CBD) into Psychotropic Cannabinoids Including Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC): A Controversy in the Scientific Literature. Toxics. 2020;8(2):41. doi:10.3390/toxics8020041
- Gülck T, Møller BL. Phytocannabinoids: Origins and Biosynthesis. Trends in Plant Science. 2020;25(10):985-1004. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2020.05.005
- Kruger DJ, Kruger JS. Delta-8-THC: Delta-9-THC’s nicer younger sibling? Journal of Cannabis Research. 2022;4(1). doi:10.1186/s42238-021-00115-8
- Kruger DJ, Kruger JS. Consumer Experiences with Delta-8-THC: Medical Use, Pharmaceutical Substitution, and Comparisons with Delta-9-THC. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. Published online November 19, 2021. doi:10.1089/can.2021.0124
- Moreno-Sanz G. Can You Pass the Acid Test? Critical Review and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid A. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research. 2016;1(1):124-130. doi:10.1089/can.2016.0008
- Nadal X, del Río C, Casano S, et al. Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a potent PPARγ agonist with neuroprotective activity. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2017;174(23):4263-4276. doi:10.1111/bph.14019
- Russo EB. Taming THC: potential cannabis synergy and phytocannabinoid-terpenoid entourage effects. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2011;163(7):1344-1364. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01238.x
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




