Key Takeaways
- Making CBD oil allows customization, fine-tuned dosing, quality assurance, and can be cost effective.
- You’ll need CBD flower, coconut or olive oil, slow cooker, glass jars, cheesecloth, a thermometer, and a funnel.
- To make: Decarb the weed > Mix into oil > Heat at ~180F for 2-3hrs > Strain > Jar and store
CBD oil, short for cannabidiol oil, is an extract from the cannabis plant. It’s currently thriving as a natural remedy used to to reduce their anxiety, improve sleep, stress relief, and improve general health and well-being.1 From grandmas to graduates, people (and pets) are finding therapeutic benefits from CBD oil without the mind-altering effects.
Like many, you may be wondering how to make CBD oil at home. Creating your own CBD oil can be incredibly rewarding. It’s cost-effective, saving you money compared to purchasing pre-made products. Plus, you have complete control over the ingredients and the process, ensuring that your CBD oil is pure and tailored to your needs.
What is CBD Oil?
CBD oil is a concentrated extract of cannabidiol mixed with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil. CBD tinctures can be oil or alcohol-based.
Significant differences exist between CBD extracts for vaping and CBD oil used for cooking or recipes. You should NOT vape CBD cooking oil. This guide focuses on creating a safe and effective CBD oil recipe for sublingual use or cooking only.
CBD oil is produced from whole plant flowers, broad-spectrum oil, or isolate. By law, hemp flower needs to have less than 0.3% THC. Whole plant flowers, available in legal cannabis states, can contain 10-15% CBD and 2-4% THC.
Commercial processors use carbon dioxide, ethanol, or solvent extraction with olive oil to minimize the risk of harmful residues. Extraction practices using hexane or butane can leave harmful residues.
CBD is popular for its health benefits. Unlike THC, its non-intoxicating effects attract those who want relief but don’t want a daily buzz. CBD achieves this because it doesn’t bind directly to cannabinoid receptors like THC. Instead, it inhibits FAAH, an enzyme responsible for breaking down anandamide, a crucial endocannabinoid in the body.2
The formulations of store-bought CBD oil are classified based on the chemical compounds they contain. Simply, they are:
- Full-Spectrum CBD: This utilizes all compounds of the cannabis plant, including CBD, terpenes, flavonoids, and other cannabinoids, with THC concentrations typically below 0.3% to meet federal guidelines.
- Broad-Spectrum CBD: Broad-spectrum CBD is similar to full-spectrum, but is nearly THC-free, making it a preferred choice for those who wish to avoid THC altogether.
- CBD Isolate: Isolate is pure CBD, typically harvested from the legal hemp varieties of cannabis, containing no other cannabinoids or plant compounds.
By understanding what goes into making CBD oil, you can better appreciate its potential benefits and how to incorporate it into your wellness routine.
Why Make CBD Oil?

Making your own CBD oil at home is a simple DIY project. With a minimal time investment, you can reap benefits for your health and wallet. A few reasons why you might consider taking on this satisfying project include:
- Customizable: One of the greatest benefits of making CBD oil at home is the ability to customize it to your needs. You can control the potency, flavor, and even the type of carrier oil used. This level of customization ensures that you get a product tailored precisely to your preferences and health requirements.
- Cost-effective: Purchasing premade CBD oil can be expensive, especially if you require higher doses for therapeutic purposes. However, making CBD oil can save you money in the long run. The cost, including kitchen tools and high-quality cannabis flower, is offset by the long-term savings of producing your oil.
- Quality assurance: You have complete control over the ingredients and process when you make CBD oil yourself. You’ll know your product is free from unwanted additives, contaminants, or low-quality ingredients.
- Therapeutic benefits: There is growing evidence of the potential health benefits of CBD oil. CBD has demonstrated potential therapeutic benefits for conditions such as epilepsy, anxiety, depression, psychotic disorders, sleep disturbances, and even certain types of cancer. Multiple studies in animals show CBD notably inhibited tumor growth in various cancers, including breast, lung, colon, prostate, colorectal, brain glioma, leukemia/lymphoma, and endocrine.3 CBD also increases the levels of anandamide (known as the bliss molecule) and is associated with mood regulation and potential anti-anxiety and antidepressant effects.4
- Rapid absorption: Sublingual or under-the-tongue delivery of CBD is particularly beneficial for symptoms needing rapid relief, such as anxiety or acute pain. This method bypasses the liver to allow faster absorption into the bloodstream than an oral method, like capsules or edibles.5
- Wide Range of Uses: You can incorporate CBD oil in recipes, make topical products, or use it sublingually. This versatility makes it easy to add to your daily routine, whether you add it to your morning smoothie or as a tincture.
Reasons Not to Make CBD Oil
Even with the advantages, making CBD oil at home might not be for everyone.
Before using CBD, consult your healthcare professional. Although generally safe for use, you shouldn’t use CBD with certain medications. CBD is metabolized via the liver when ingested and can alter the effectiveness of certain drugs. Combined with certain medicines, high doses of CBD may cause liver abnormalities.
CBD can have side effects. Although generally mild, side effects can include nausea, tiredness, or digestive issues.6 Too much MCT oil (medium-chain triglycerides) or other carrier oils can cause an upset stomach. With CBD or any supplement, be careful if you experience adverse effects.
Making a CBD oil recipe isn’t difficult if you’re reasonably comfortable in the kitchen. However, it does require an investment of time. The kitchen equipment needed isn’t expensive, but it may not be in everyone’s cupboard. Purchasing these tools can be an additional expense.
All oils have a shelf life, or the period of time during which they remain stable before becoming rancid. Homemade CBD oil requires a carrier oil, which can be almost any edible oil. When combined with CBD flower, the oil enhances the absorption and bioavailability of the cannabinoid. Making CBD oil in large quantities can be wasteful if not used within a reasonable time frame.
Without lab testing or expensive home testing equipment, gauging the exact potency of homemade CBD oil can be challenging. While edible dosage calculators are helpful, they may not be a perfect translation of CBD oil dosages and may not measure with precision. If a strict dosage protocol is required or you are uncomfortable with a moderate variation in potency, you might prefer a commercially prepared, lab-tested compound.
Given the time and variability involved in making CBD oil at home, many patients purchase it from reputable sources instead. Commercially available CBD oils are typically lab-tested for quality and potency, ensuring a safe product and consistent dosage. This convenience can outweigh the benefits of making their oil for some people.
What You Need to Make CBD Oil at Home
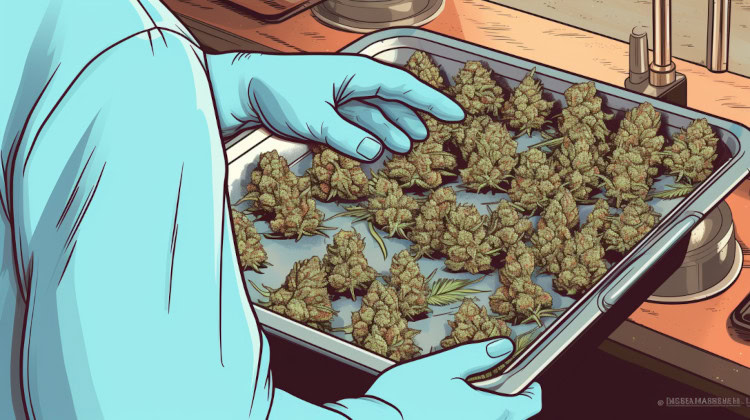

Creating CBD oil at home is easy but requires specific supplies and some know-how. Here’s a rundown of what you’ll need and an overview of the process.
There are four main steps to making CBD oil. You’ll need to decarboxylate the cannabis, infuse it into a carrier oil, and properly strain and store the final product. To begin, you’ll need these supplies:
- High-CBD cannabis flower
- Carrier oil common options include coconut, olive, or MCT oil
- Double boiler or slow cooker
- Cheesecloth or fine strainer
- Glass jars (canning jars are a great option)
- Oven and baking sheet for decarboxylating the cannabis
- Thermometer
- Funnel (optional)
How to Make CBD Oil at Home
Once you’re ready to make your own CBD oil, you can follow these step-by-step instructions.
- Decarboxylate the Cannabis: Preheat your oven to 250°F (120°C). Break the cannabis into small pieces and spread it on a baking sheet. Bake in a preheated oven for 25-40 minutes, stirring occasionally to ensure even heating.
- Combine with Carrier Oil: Add the decarboxylated cannabis to your double boiler or slow cooker. Pour in enough carrier oil to fully submerge the cannabis. Typically, a 1:1 ratio of cannabis to oil is used, but you can adjust based on your desired potency. A double boiler or slow cooker helps maintain a consistent, low temperature.
- Heat and Infuse: Simmer on low heat for 2-3 hours, stirring occasionally. To avoid degrading the cannabinoids, the temperature should remain between 160-200°F (70-93°C). Using a thermometer can help maintain the correct temperature.
- Strain the Mixture: Once the infusion is complete, strain the mixture through a cheesecloth or fine strainer into a clean glass jar. Squeeze the cheesecloth to extract as much oil as possible from the plant material.
- Store the CBD Oil: Store the finished CBD oil in a cool, dark place to maintain its potency and shelf life. Glass jars with tight-sealing lids work best. Label the jars with the date and type of carrier oil used for future reference.
Other Options for CBD Oil
Making CBD oil at home can be more cost-effective if you plan to use it regularly and in larger quantities. If you don’t want to invest in the time and equipment, purchasing CBD oil can be cheaper in the short term, especially if you only need small amounts.
Isolate CBD bought in bulk can be used to make CBD oil. Although isolate may be less expensive than high-quality CBD flower, you’ll miss out on the full benefits of terpenes, flavonoids, essential oils, and other cannabinoids.
CBD oil is available from licensed dispensaries, storefronts, and online retailers. These products are convenient and accessible, especially if you need CBD oil immediately or prefer not to DIY. You can find a wide variety in various strengths, flavors, and formulations, making it easy to find one that suits your preferences and needs.
Consider CBD-infused products, such as gummies, capsules, creams, and beverages for an occasional CBD boost. CBD-infused beverages like CBD coffee may offer a morning boost, while CBD water provides hydration with potentially added benefits. Water-soluble CBD isolate powder blends easily and can add a CBD note to beverages, foods, or topicals.
Whether homemade or store-bought, CBD oil products allow you to tailor your wellness plan to your specific needs and preferences.
References
- Moltke J, Hindocha C. Reasons for cannabidiol use: a cross-sectional study of CBD users, focusing on self-perceived stress, anxiety, and sleep problems. Journal of Cannabis Research. 2021;3(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00061-5 ↩︎
- Cather JC, Cather JC. Cannabidiol primer for healthcare professionals. Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings. 2020;33(3):376-379. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2020.1775437 ↩︎
- Peng J, Fan M, An C, Ni F, Huang W, Luo J. A narrative review of molecular mechanism and therapeutic effect of cannabidiol (CBD). Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 2022;130(4):439-456. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13710 ↩︎
- Martin-Santos R, Crippa JA, Batalla A, et al. Acute Effects of a Single, Oral dose of d9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) Administration in Healthy Volunteers. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2012;18(32):4966-4979. https://www.eurekaselect.com/article/45750 ↩︎
- Lucas CJ, Galettis P, Schneider J. The pharmacokinetics and the pharmacodynamics of cannabinoids. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2018;84(11):2477-2482. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.13710 ↩︎
- Huestis MA, Solimini R, Pichini S, Pacifici R, Carlier J, Busardò FP. Cannabidiol Adverse Effects and Toxicity. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2019;17(10):974-989. doi:10.2174/1570159X17666190603171901 ↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




