Key Takeaways
- Terpinolene is a terpene found in pine, apples, nutmeg, and cannabis.
- It may have an energizing and creativity boosting effect as well as antimicrobial properties.
- This terpene has a complex scent that’s often described as piney or woodsy.
Terpinolene is a terpene found abundantly in apples, sage, turmeric leaves, pines, nutmeg, cardamom, and some cannabis cultivars. It gives off floral, citrus, and pine scents and is known for its overall fresh fragrance. Terpinolene's possible benefits and effects (all of which require further study) include being antibacterial, antimicrobial, antifungal, sedative, and pain reducer.
While many commercially available strains have relatively low levels of terpinolene—far lower than the quantities used in preliminary studies about the terpene’s potential benefits—this may assist (via the entourage effect) in determining the effects, flavors and aromas of some of the most coveted cannabis strains.
How Does Terpinolene Work?
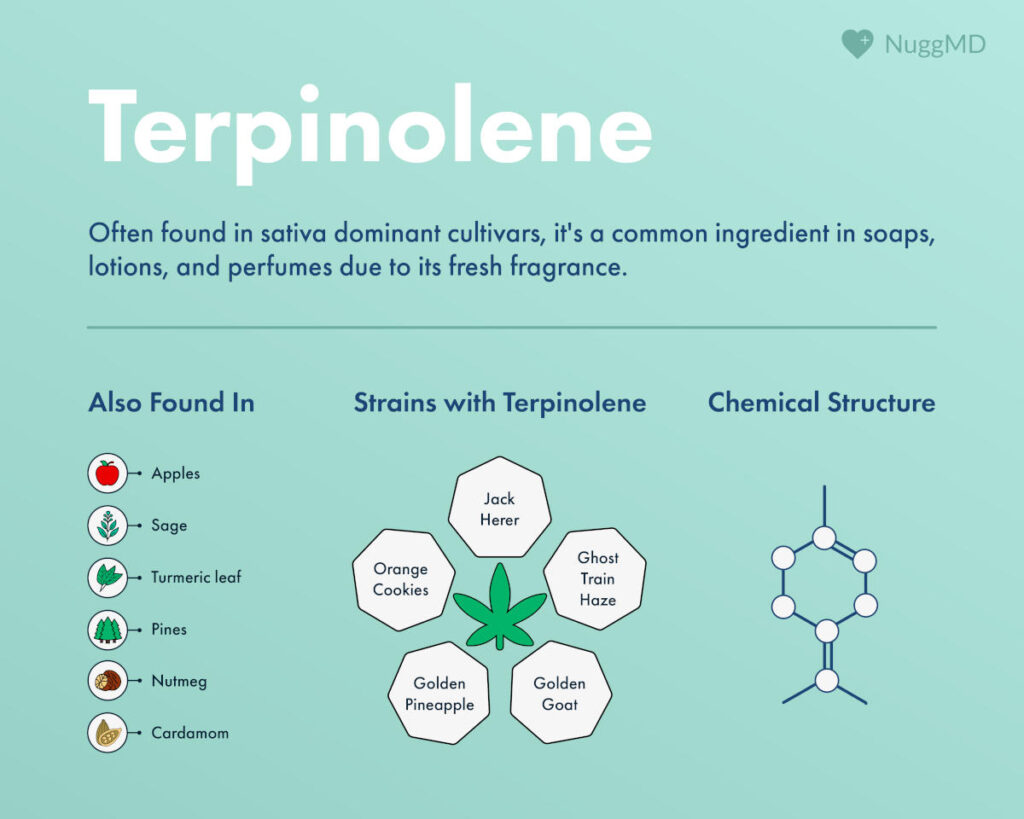
Scientists refer to terpinolene as alpha-terpinolene or TPO. It is a monocyclic monoterpene, a single ring of atoms extracted from plants. In nature, terpinolene is considered a primary terpene because it is abundant in many plants and herbs, such as lilac, nutmeg, cumin, tea tree, and sage. In cannabis, it is less common, appearing as the dominant terpene in about 1 in 10 strains.
Terpinolene is very much a supporting player in the cannabis plant and is often found in sativa-labeled cultivars.
A 2013 study found that terpinolene, on its own, provided mice with sedating effects.1 However, in high terpinolene strains, the user-reported effects are often more energizing and creative.2 This may be the result of the entourage effect and the way terpinolene interacts with other terpenes and cannabinoids, but more research is needed.
Potential Benefits of Terpinolene

Terpinolene has demonstrated antioxidant properties, and the terpene is found in research to offer potential antibacterial, antifungal, and antimicrobial properties. Emerging research has also suggested that terpinolene may help reduce the proliferation of cancer cells in rats. However, early-stage studies often lack the human trials, number of participants, and peer review necessary to claim a definitive benefit.
Here are a few interesting studies to better understand the direction modern research is taking:
- A 2005 study found that terpinolene may be a means of treating heart disease when combined with other flavonoids by preventing the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or bad cholesterol resulting from damage by free radicals.3
- In a study done in 2013, researchers observed that terpinolene may help to reduce the spread of brain tumor cells in rats.4
- Researchers have found that terpinolene’s antibacterial and antifungal properties may make it an effective agent against staphylococcus aureus (staph) and Escherichia coli (E. coli). It was even found to be effective against Propionibacterium, which is responsible for causing acne.5
- There is also interesting research that shows that terpinolene may help repel pests like mosquitos.6
While these preliminary findings are exciting, consumers should note that terpinolene is not an accepted treatment for any of these conditions.
Cannabis Strains High in Terpinolene

Terpinolene's scent is complex, with notes ranging from piney to woodsy. Its fresh fragrance has made terpinolene a common ingredient in soaps, lotions, and perfumes. Beyond its fresh scent, its status as an antioxidant makes it a common addition to beauty products that aim to brighten the skin, increase moisture, and reduce fine lines.
Although research has shown that it has sedating effects on mice, terpinolene strains are often sought after for their uplifting, creative, energetic effects.
Strains that test high in terpinolene are rare but include:
These cultivars are all THC-dominant. Most are labeled as a “Sativa,” with piney, citrusy, and tropical aromas that often provide feelings of euphoria and energy (though the effects may vary depending on the consumer and the genetic make-up of each cultivar).
Orange Cookies is considered a hybrid. It is a cross between Orange Juice – a talkative limonene-rich strain, and Girl Scout Cookies – a relaxing caryophyllene-rich strain, which could be the reason for the more mellow effects of the resulting cultivar.
Although terpinolene is plentiful in nature, it is harder to find in cannabis products. It provides strong smells of crispy freshness in both contexts with floral, piney, and citrus notes. When found in cannabis, terpinolene effects are most often classified as happy, euphoric, and energetic.
While terpinolene has been linked to a range of potential benefits, including promising studies around reducing the proliferation of cancer cells, these studies are often limited in scope and have not been replicated in human trials. Further research is needed to fully understand the benefits of terpinolene in humans (and to determine if any of the reported benefits can be achieved from the quantities of terpinolene found in cannabis plants).
Resources
- Ito K, Ito M. The sedative effect of inhaled terpinolene in mice and its structure–activity relationships. Journal of natural medicines. 2013;67(4):833-837. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-012-0732-1 ↩︎
- Lewis MA, Russo EB, Smith KM. Pharmacological Foundations of Cannabis Chemovars. Planta Medica. 2017;84(04):225-233. doi:10.1055/s-0043-122240 ↩︎
- Grassmann J, Hippeli S, Spitzenberger R, Elstner EF. The monoterpene terpinolene from the oil of Pinus mugo L. in concert with alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene effectively prevents oxidation of LDL. Phytomedicine. 2005;12(6-7):416-423. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2003.10.005 ↩︎
- Aydin E, Türkez H, Taşdemir S. Anticancer and antioxidant properties of terpinolene in rat brain cells. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2013;64(3):415-424. doi:10.2478/10004-1254-64-2013-2365 ↩︎
- Eftekhar F, Yousefzadi M, Azizian D, Sonboli A, Salehi P. Essential Oil Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Diplotaenia damavandica. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C. 2005;60(11-12):821-825. doi:https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2005-11-1202
↩︎ - Wang JL, Li Y, Lei CL. Evaluation of monoterpenes for the control of Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) and Sitophilus zeamaise Motschulsky. Nat Prod Res. 2009;23(12):1080-1088. doi:10.1080/14786410802267759 ↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.