In This Article
- What is THCP?
- What are the Effects and Benefits of THCP?
- How Strong is THCP?
- What are the Risks and Drawbacks of THCP?
- THCP vs THC: How Are They Different?
- THCP vs Delta-8
- THCP vs THCO
- Where is THCP present?
- Is THCP legal?
- What products contain THCP?
- How long does it take THCP to take effect?
- How long does the effect of THCP last?
- How long does THCP stay within the body?
- References
Major cannabinoids like THC and CBD have long dominated the cannabis market, with many options for consumers to choose from. Lately, with the recent passing of the Farm Bill in 2018, minor hemp-derived semi-synthetic cannabinoids like delta-8 have started to make their way into products.
While it may be easy to research the potential effects you may feel from well-known cannabinoids, accurate information on the lesser-known minor ones can be difficult to find. Before you consume THCP products, it’s essential to your safety and the experience to know what to expect.
What is THCP?
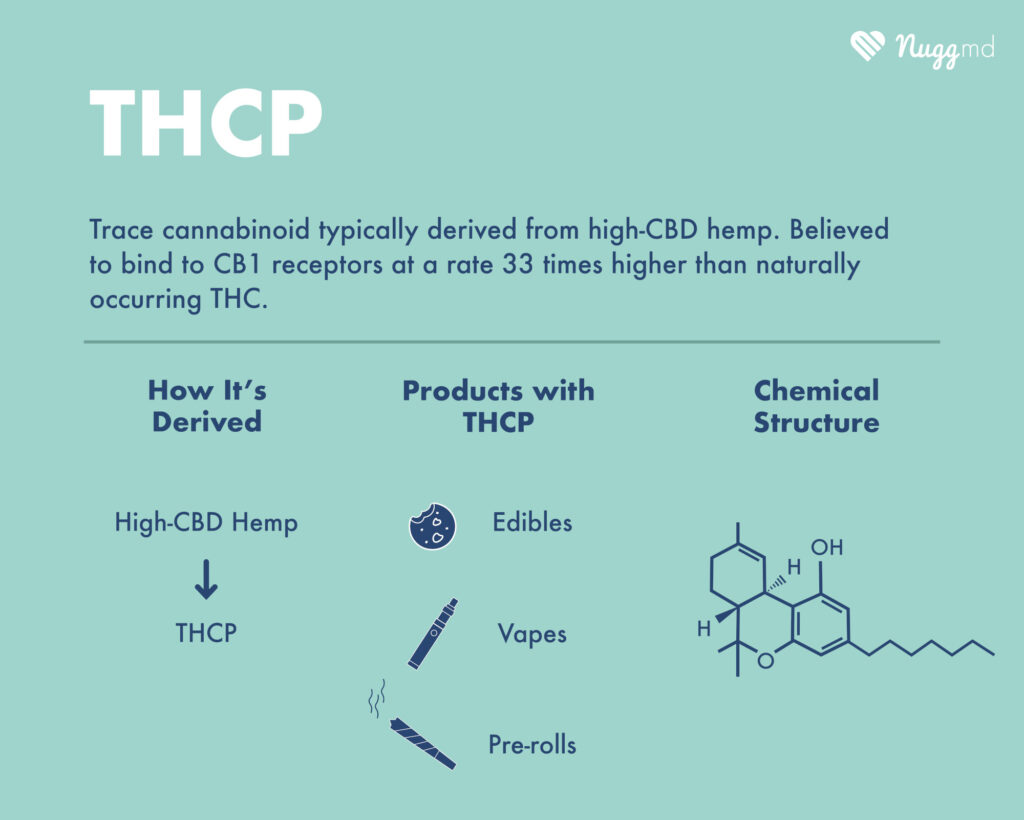
THCP is the acronym for trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol. It can also be referenced as Δ9-THCP or delta-9-THCP. It is a non-natural cannabinoid found in the plant, so manufacturers synthesize THCP using a method that typically involves harsh processing conditions. THCP is not derived from hemp or converted from the CBD found in hemp.
The research on THCP is limited to one study done in 2019. The cannabinoid was unintentionally discovered, but researchers observed it has a longer seven-term side alkyl chain than the 5-term side alkyl chain of THC.
They also found that THCP binds to the CB1 and CB2 receptors of the endocannabinoid system. The CB1 receptor is responsible for mediating the intoxicating effects of cannabis, and the CB2 receptors affect the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions.
THCP binds to the CB1 receptors at a higher rate than the CB2 receptors and mimics THC-like effects. This study was done in cell lines, and researchers believe it may indicate the potential for it to have similar benefits to THC when isolated and consumed.1
What are the Effects and Benefits of THCP?

There is little known about the properties of THCP beyond the single study done in 2019. Researchers understand the cannabinoid’s chemical structure and that it has the potential to bind to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. When tested on mice, the cannabinoid decreased locomotor activity and rectal temperature, induced catalepsy (a trance-like state characterized by loss of voluntary motion and increased stiffness), and produced pain-relieving effects.
The specific effects of how THCP feels when isolated and consumed by humans are still unclear, but researchers believe it has similar effects to THC. The cannabinoid is naturally found in such low concentrations that it is synthesized from CBD.
Despite the need for more understanding about how humans react to THCP, it has still made its way into purchasable consumable goods.
Online documentation of how the cannabinoid feels is often associated with brands marketing their products with vague or little consumer feedback to support their claims. In-depth testimonials are hard to find, but one Reddit user posted a time-stamped journal-like description of their experience with THCP. The user detailed the titrated dosages they consumed over a few hours and reported that THCP edibles changed their perception of sensations like temperature and taste while enhancing their mood and decreasing pain levels.
This account is just one consumer’s experience in an uncontrolled setting. Still, combined with what researchers understand about THCP, consumers should be mindful of its ability to cause intoxicating effects similar to THC.
It remains relatively unclear what the specific THCP effects are when consumed by humans, so it may be best to use what is known about THC as a general guideline for what you might feel. THC’s potentially beneficial effects include relaxation, euphoria, and increased appetite.2
THCP may be a cannabinoid with benefits that can be felt in small doses. Researchers also found that due to its seven-term chain, it binds to the CB1 receptor at 33 times the strength that THC does and is active at lower doses.
How Strong is THCP?
Researchers in the 2019 study mentioned that the molecular structure of the cannabinoid may be the reason it binds to the endocannabinoid receptors at a much higher affinity – suggesting it's stronger than THC, meaning you may need 5mg THCP to feel the same effects of taking 10mg THC.
Since THC causes intoxicating effects, consumers should exercise caution when taking THCP, especially if they’re consuming THCP edibles.
The intensified potency level is reason enough for consumers to take caution and practice the “go low and slow” motto – start with small doses and wait some time to feel the full effects before increasing the dosage if you feel comfortable or compelled to do so.
What are the Risks and Drawbacks of THCP?

There is little research on THCP, so there are currently few known or documented risks.
The researchers who discovered THCP documented that one of the negative side effects the mice in the study experienced was catalepsy, a daze-like state accompanied by loss of voluntary motion and increased body stiffness. There is currently no research or documented accounts of this happening in humans.
Something for consumers also to consider is that most, if not all, of the THCP available to consumers is synthesized using other compounds. This process typically involves harsh processing conditions and chemicals that may result in low-quality products and possible contamination.
One study purchased ten vape pens and examined them for impurities, and most tested positive for contaminants in higher levels than what was listed on their certificate of analysis. The researchers attributed these impurities to low-quality hemp feedstock being used, poor post-reaction purification, and inadequate impurity testing.3
THCP is synthetic, as it is created in a lab through chemical synthesis. It’s important to note that the CDC advises that users exercise caution when consuming synthetic cannabinoids like spice or K2. They don’t interact with the body well and may cause adverse side effects like rapid heart rate, vomiting, agitation, confusion, and hallucinations. Delta-8, a semi-synthetic cannabinoid, has been found to have similar side effects to synthetic cannabinoids in some studies.
The potential potency of the cannabinoid may be the most important risk to state as it may induce more intensified effects – both beneficial and adverse – than consumers are expecting.
The potency of THCP may benefit consumers and patients with a high tolerance level or a need for stronger effects to get to their desired feelings. It also may be helpful if consumers don’t want to consume a lot of smoke or other additives and ingredients in their infused products. The drawbacks of THCP may come from overconsumption or its interaction with other chemical compounds in the cannabis product.
Since the benefits and risks haven’t been well studied, it is best to be mindful of the THCP products you consume if you do decide to do so – both the quality and potency. Consumers should keep in mind that THCP may produce effects at a much higher intensity than that of THC.
THCP vs THC: How Are They Different?
Although THC and THCP seem to have similar effects, a few factors differentiate them.
- Chemistry. THC has a 5-term side alkyl chain, while THCP is a 7-term chain.
- Source. THC is a naturally produced cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant, while THCP is chemically created in a lab through synthesis.
- Effects. What is known about THCP effects was discovered in in-vitro studies and tested on mice. The cannabinoid inducted reduced pain and affected body temperature and mobility.
- Potency. Researchers found that THCP binds to CB1 receptors at a rate 33 times higher than THC, making it more potent.1
- Length of effect. The duration of THCPs effects is unknown and may be closely related to how the cannabinoid is consumed.
THCP vs Delta-8

Delta-8 is currently the most popular hemp-derived cannabinoid. Similarly to THCP, it is known to cause effects that mimic THC, but all three are unique in their chemical structure and intensity of effects.
- Chemistry. The molecular structure of these cannabinoids is where their differences begin. THC and delta-8 have the same molecular structure; only where their double bond is located is different. THC’s double bond is on the 9th chain, while delta-8 is, as you might guess, on the 8th carbon chain.4 THC and delta-8 both have a 5-term side alkyl chain, while THCP has a 7-side alkyl chain.
- Source. THCP is created through chemical synthesis, while delta-8 may be found naturally as degraded compounds in the plant in trace amounts.
- Effects. THCP has been found to possibly have pain-relieving properties and affect body functions like temperature and mobility.1 There is little research on delta-8's effects, but there is a good amount of consumer testimonials. Some users report feelings of relaxation, pain relief, and euphoria.
- Potency. While THCP binds to the CB1 receptors at a higher rate than THC, delta-8 does at a lower rate, meaning the effects may be similar to THC but not as intense.1,4
THCP vs THCO
THCO is a fully synthetic, or non-natural, cannabinoid that has a long but vague history dating back to before the 1970s. It is considered an acetate and can also be referred to as delta-8 acetate or THCO acetate. Its synthetic status caused the Drug Enforcement Administration to classify it as a controlled illegal substance in 2023.
THCO’s molecular structure looks a little similar to THC’s structure, but there are a few significant differences between the bonds. THCO is an acetate ester of THC, which is produced through a chemical process called acetylation that involves adding an acetyl functional group into a chemical compound, which substitutes the acetyl group for a hydrogen atom. It is derived from hemp, like THCP and delta-8, but it isn’t found in the cannabis plant naturally, and despite its long history, there is still limited research on its effects and potency.
It is believed that THCO causes more psychedelic effects rather than intoxicating ones like THC. One of the only studies done on THCO was recently published in 2023 and found that most participants felt little to no psychedelic experiences. Researchers noted that those who did feel psychedelic effects may have been more influenced by contaminants or expectations rather than the THCO itself.5
THCO is a fully synthetic cannabinoid that medical professionals recommend using caution when consuming due to the high risk of potential adverse side effects. THCO is an acetate with a similar structure to the vitamin E acetate found in many counterfeit vapes that caused serious harm and even death to some consumers. One study found that when acetates like THCO are vaped, they produce ketene, a toxic gas that can damage the lungs.6
The potency of THCO is also up for debate. One review of online responses found that some users felt it was significantly more potent than THC, while others felt it was weaker.7 Research is still needed to understand the risks, effects, and potency levels of cannabinoids like THCO and THCP.

Where is THCP present?
THCP is not found in the cannabis plant and is created through a chemical synthesis process.
Is THCP legal?
THCP is legal in all places that allow the sale of hemp-derived cannabinoids like delta-8.
What products contain THCP?
THCP can be infused into typical cannabis products like edibles and vapes. It has even been found isolated and infused into pre-rolls.
How long does it take THCP to take effect?
Using the time frames for THC as a guide, the onset time length depends on how the product is consumed. Edibles will probably take anywhere from 30 minutes to two hours, while vapes and prerolls may take effect within a few moments.
How long does the effect of THCP last?
The duration of the effects will likely depend on how the product is consumed. Edibles effects will likely last anywhere from 6 to 12 hours, while vapes and pre-rolls may only last a few hours.
How long does THCP stay within the body?
It is unknown how long THCP will stay in the body, but it may be safe to assume it can last for similar lengths in the system as THC and CBD. Depending on the frequency and consumption method, cannabinoids can stay in the system for as little as 24 hours to upwards of a month.
References
- Citti C, Linciano P, Russo F, et al. A novel phytocannabinoid isolated from Cannabis sativa L. with an in vivo cannabimimetic activity higher than Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiphorol. Scientific Reports. 2019;9(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56785-1
↩︎ - Sharma P, Murthy P, Bharath MM. Chemistry, metabolism, and toxicology of cannabis: clinical implications. Iran J Psychiatry. 2012;7(4):149-156.
↩︎ - Ray CL, Bylo MP, Pescaglia J, Gawenis JA, Greenlief CM. Delta-8 Tetrahydrocannabinol Product Impurities. Molecules. 2022;27(20):6924. Published 2022 Oct 15. doi:10.3390/molecules27206924
↩︎ - Kruger JS, Kruger DJ. Delta-8-THC: Delta-9-THC’s nicer younger sibling? Journal of Cannabis Research. 2022;4(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s42238-021-00115-8
↩︎ - Kruger DJ, Bone C, Meacham MC, Klein CH, Kruger J. THC-O-Acetate: Scarce Evidence for a Psychedelic Cannabinoid. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. Published online June 29, 2023:1-5. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2023.2230573
↩︎ - Munger KR, Jensen RP, Strongin RM. Vaping Cannabinoid Acetates Leads to Ketene Formation. Chemical Research in Toxicology. 2022;35(7):1202-1205. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.2c00170
↩︎ - Kruger DJ, Amila K, Kaplan SM, et al. A Content Analysis of Social Media Discussions on THC-O-Acetate. Cannabis. 2023;6(2):13-21. Published 2023 Jul 5. doi:10.26828/cannabis/2023/000164
↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




