The world of cannabinoids has experienced a remarkable boom in recent years as scientists delve deeper into the vast array of compounds found in cannabis. With the passing of the 2018 Farm Bill, which played a significant role in this expansion, a Pandora's box of novel cannabinoids has been explored. One such intriguing cannabinoid is THCJD, which is captivating enthusiasts and researchers alike with its fascinating properties.
THCJD, also known as tetrahydrocannabioctyl, is a newly rediscovered cannabinoid that has garnered attention, especially from hemp product manufacturers. What sets THCJD apart is its reportedly "unique psychedelic effect," which has gained recognition for being genuinely distinctive. According to some anecdotal reports, THCJD is a staggering 19 times more intoxicating than THC.
But just how strong is THCJD? And what are the benefits and risks of this relatively unknown cannabinoid?
What is THCJD?
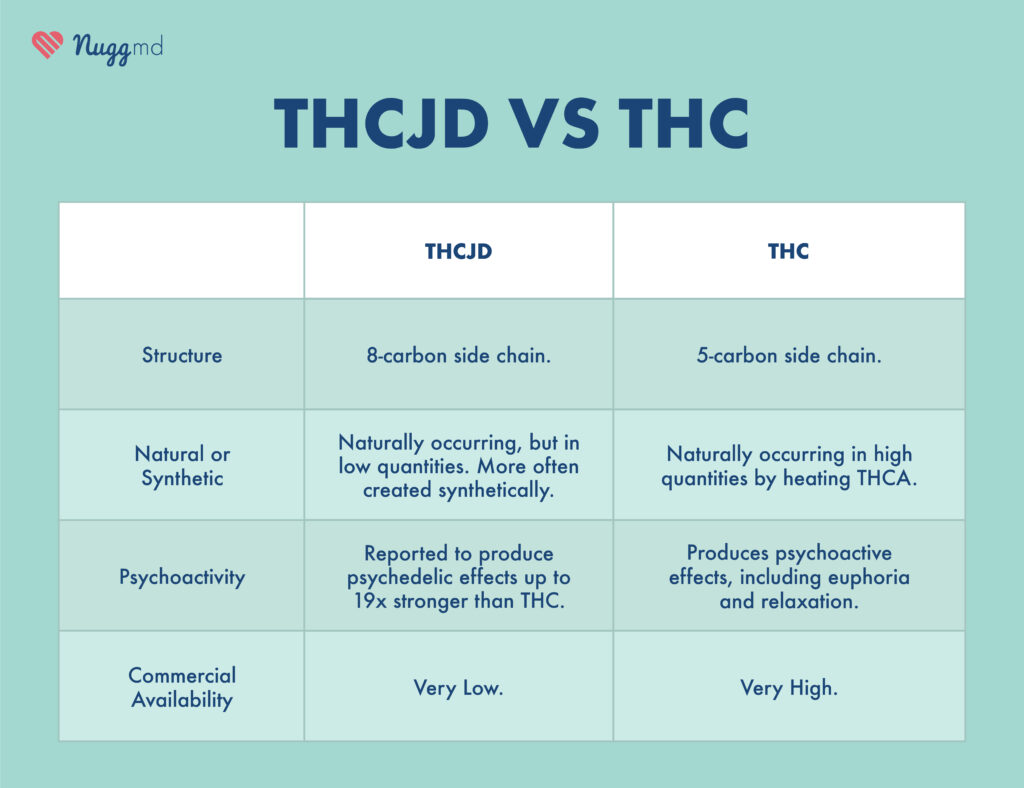
THCJD stands out due to its distinct chemical structure. It possesses an eight-carbon side chain, which sets it apart from other cannabinoids. This structural difference contributes to its unique properties and creates intriguing effects.
While there are many claims that this cannabinoid naturally occurs in the plant, there is no evidence to suggest this is the case. Similarly, many articles state this is a newly discovered cannabinoid. However, this particular isomer was identified in 1941 as Tetrahydrocannabioctyl (THC-Octyl or delta 8-THC-C8). Interestingly, this cannabinoid is recognized as being the synthetic cannabinoid, JWH-138. Unlike THC and CBD, which are more prevalent and well-studied, THCJD is considered a minor cannabinoid due to its limited quantity.1
Because THCJD is not found within cannabis plants, it is synthesized in a lab to produce the quantities needed to make cannabis products. This makes it similar to other cannabinoids like delta-8 and delta-10.
The scientific literature dedicated to this compound is highly sparse, bordering on non-existent. So, with such a shroud of mystery, it's difficult to draw any solid conclusions about this chemical: what it is, what it does, its effects, benefits, risks, and whether it is a reasonable alternative to traditional THC products.
What are the Effects of THCJD?

Perhaps the most notable effect of THCJD is the reported "psychedelic-like" effects of the compound. Meaning THCJD reportedly mimics the effects of psychedelics like psilocybin. Many cannabinoids are, at most, merely intoxicating, which means they can alter perception, mood, and cognition.
However, some claim that THCJD can go beyond intoxicating due to its high potency. Some report that it is 19 times more intoxicating than THC, and with such heightened potential for intoxication, THCJD may induce more potent intoxicating – or even psychedelic – effects than THC or other cannabinoids.
The scientific literature on this “new” cannabinoid is virtually non-existent, so no objective claims about its potency can genuinely be made at this point. However, THCJD’s reported strength is presumed to be due to its chemical structure and the way that structure interacts with the endocannabinoid system.
Both THC and THCJD interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the body, but they may differ in their binding affinity to specific cannabinoid receptors. THC primarily binds to the CB1 receptors in the brain and nervous system, leading to its intoxicating effects.2 However, THCJD's unique eight-carbon side chain structure may contribute to its distinctive effects. Research indicates that the longer a compound’s carbon chain length, the more affinity it may have for binding to the CB1 receptor. For context, THC and CBD have 5-carbon side chain structures.3
While more research is required to explore its specific mechanisms fully, the structural difference may result in unique interactions with cannabinoid receptors or other biological targets.
How Potent is THCJD?
THCJD has been hailed for its remarkable potency, with reports suggesting it’s approximately 19 times more intoxicating than delta-9 THC. This makes THCJD similar to another cannabinoid, THC-P, which is reportedly three times stronger than THC. However, scientific studies still do not verify these claims, so it's difficult to gauge how potent THCJD is.
Thus, THCJD lies in stark contrast to delta-9 THC, which is, by far, the most well-known and extensively studied intoxicating cannabinoid.
While THCJD's potency is certainly high enough to raise a few eyebrows, remember that several other potent cannabinoids exist, such as THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin) and THC-O (tetrahydrocannabinol-O-acetate). THCV is known for its potential appetite-suppressing and energizing effects.2 At the same time, THC-O is a highly potent synthetic analog of delta-9 THC, reported to be even more potent than both THC and THCJD. However, a study published in 2023 found that 79% of those who used THC-O found it had little to no psychedelic effect.4
What are the Benefits of THCJD?

THCJD's potentially high potency suggests that it may offer a high-dose alternative to individuals seeking stronger intoxicating experiences. The unique psychedelic effect reportedly associated with THCJD may also appeal to those interested in exploring altered states of consciousness.
While further research is needed, it is possible that THCJD, like other cannabinoids, may have potential therapeutic properties. Exploring THCJD's interaction with the endocannabinoid system could unveil novel applications in pain management, mood disorders, and neuroprotection.
What are the Risks and Drawbacks of THCJD?
As with any substance, it's crucial to consider the potential risks and drawbacks associated with THCJD.
The most significant benefit of the compound may also be its greatest risk: the heightened potency of THCJD may increase the risk of intoxication and impairment. Individuals should be cautious and aware of the potential effects on cognitive function, coordination, and decision-making abilities.
Beyond that, the current lack of regulation surrounding THCJD and other minor cannabinoids poses risks in terms of product quality, consistency, and accurate labeling. This can make it challenging for consumers to obtain reliable and safe products.
Assuming THCJD is lab-made, there are also inherent risks associated with the production of synthetic or semi-synthetic cannabinoids.5 These risks include potential chemical composition, purity variations, and unforeseen side effects due to the lack of comprehensive long-term studies.
Specific side effects of THCJD are yet to be extensively documented. However, it is reasonable to assume that common side effects associated with cannabinoids, such as dry mouth, red eyes, dizziness, increased heart rate, and mood changes, could potentially be experienced with THCJD use.
THCJD vs THC: How Are They Different?
When comparing THCJD and THC (delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol), several key factors set them apart.
First and foremost, at a molecular level, THC possesses a 5-carbon side chain, while THCJD stands out with its 8-carbon side chain. This structural distinction is likely the core reason behind THCJD's unique and potentially powerful effects.3
It is unknown if THCJD truly exists in the cannabis plant like THC does, as there is little research on the cannabinoid. What we do have suggests it is a semi-synthetic analog produced through the conversion of other cannabinoids, like CBD or delta-8 THC.
THC is widely known for its intoxicating effects, including euphoria, relaxation, altered perception, and increased appetite. THCJD, on the other hand, is reported to produce a unique psychedelic effect, making it stand out in terms of its intoxicating properties. However, the specific nature of THCJD's effects is an area of ongoing research.
One notable difference between THC and THCJD is their potency. THCJD is reported to be approximately 19 times more intoxicating than THC.
The duration of effects can vary among individuals and depends on various factors such as dosage and method of consumption. Generally, THC's effects are known to last for a few hours, while the specific duration of THCJD's effects is not yet well-established and requires further research.
THCJD vs THC-O
THC-O is often marketed as being approximately three times more potent than THC. While specific scientific studies confirming this claim are limited, it remains a recurring statement in various articles and publications, though user surveys published in 2023 state that over 79% of users felt limited to no psychedelic effect from THC-O.4 THCJD, on the other hand, is reported to be approximately 19 times more intoxicating than delta-9 THC.
THC-O and THCJD may differ in their effects due to variations in their chemical structures and binding affinities to cannabinoid receptors.6 THC-O and THCJD are both semi-synthetically produced cannabinoids using chemical conversions of other cannabinoids.
Unfortunately, scientific studies explicitly comparing the effects of THC-O and THCJD are currently limited, and more research is needed to understand the full extent of their individual effects and potential differences.
THCJD vs THCP
THCP (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol) is often referred to as a highly potent phytocannabinoid.7 While specific scientific studies verifying its potency compared to THC are limited, various sources suggest that THCP may be significantly more potent. Some references state that THCP could be approximately 33 times more potent than THC. However, it is essential to note that further scientific research is needed to establish the precise potency of THCP.
THCJD, on the other hand, is reported to be approximately 19 times more intoxicating than THC. While this indicates high potency compared to THC, it may still be lower than the potential potency of THCP if the 33x claim holds true.
THCP has been found to exhibit cannabimimetic activity similar to THC, meaning it also interacts with the endocannabinoid system. In pharmacological tests, THCP induced hypomotility, analgesia, catalepsy, and decreased rectal temperature, which are characteristic effects of THC.
However, the specific effects of THCJD in comparison to THCP and THC are not extensively documented in available scientific studies. Given THCJD's high potency compared to THC, it is assumed to induce more potent intoxicating effects when compared to THC.
THCJD FAQ
Is THCJD legal?
The legal status of THCJD can vary depending on local regulations. However, it does fall under the 2018 Farm Bill as a hemp derivative and is, therefore, legal on the federal level.
What products contain THCJD?
THCJD may be found in hemp-derived products, such as concentrates, edibles, and tinctures. However, it typically appears in the form of gummies and vape cartridges.
How long does it take THCJD to take effect?
The onset time of THCJD's effects may vary depending on factors such as the method of consumption and individual metabolism. Generally, effects may be felt within minutes to an hour after consumption, depending on the THCJD product consumed.
How long do the effects of THCJD last?
The duration of THCJD's effects may vary among individuals and depends on dosage, tolerance, and metabolism. Typically, the effects may last for 1 to 4 hours.
How long does THCJD stay within the body?
The exact time frame for THCJD to clear from the body may vary depending on various factors, including frequency of use, dosage, and individual metabolism. As a general estimate, it may take several days to weeks for THCJD to be eliminated.
References
- Walsh KB, McKinney AE, Holmes AE. Minor Cannabinoids: Biosynthesis, Molecular Pharmacology and Potential Therapeutic Uses. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2021;12. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.777804
↩︎ - Pertwee RG. The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2008;153(2):199-215. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707442
↩︎ - Bow EW, Rimoldi JM. The Structure-Function Relationships of Classical Cannabinoids: CB1/CB2 Modulation. Perspect Medicin Chem. 2016;8:17-39. Published 2016 Jun 28. doi:10.4137/PMC.S32171
↩︎ - Kruger DJ, Bone CC, Meacham MC, Klein C, Kruger JS. THC-O-Acetate: Scarce Evidence for a Psychedelic Cannabinoid [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jun 29]. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2023;1-5. doi:10.1080/02791072.2023.2230573
↩︎ - Cohen K, Weinstein AM. Synthetic and Non-synthetic Cannabinoid Drugs and Their Adverse Effects-A Review From Public Health Prospective. Frontiers in Public Health. 2018;6(162). doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00162
↩︎ - McPartland JM, Glass M, Pertwee RG. Meta-analysis of cannabinoid ligand binding affinity and receptor distribution: interspecies differences. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2009;152(5):583-593. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707399
↩︎ - Citti C, Linciano P, Russo F, et al. A novel phytocannabinoid isolated from Cannabis sativa L. with an in vivo cannabimimetic activity higher than Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabiphorol. Scientific Reports. 2019;9(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56785-1
↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.




