Key Takeaways
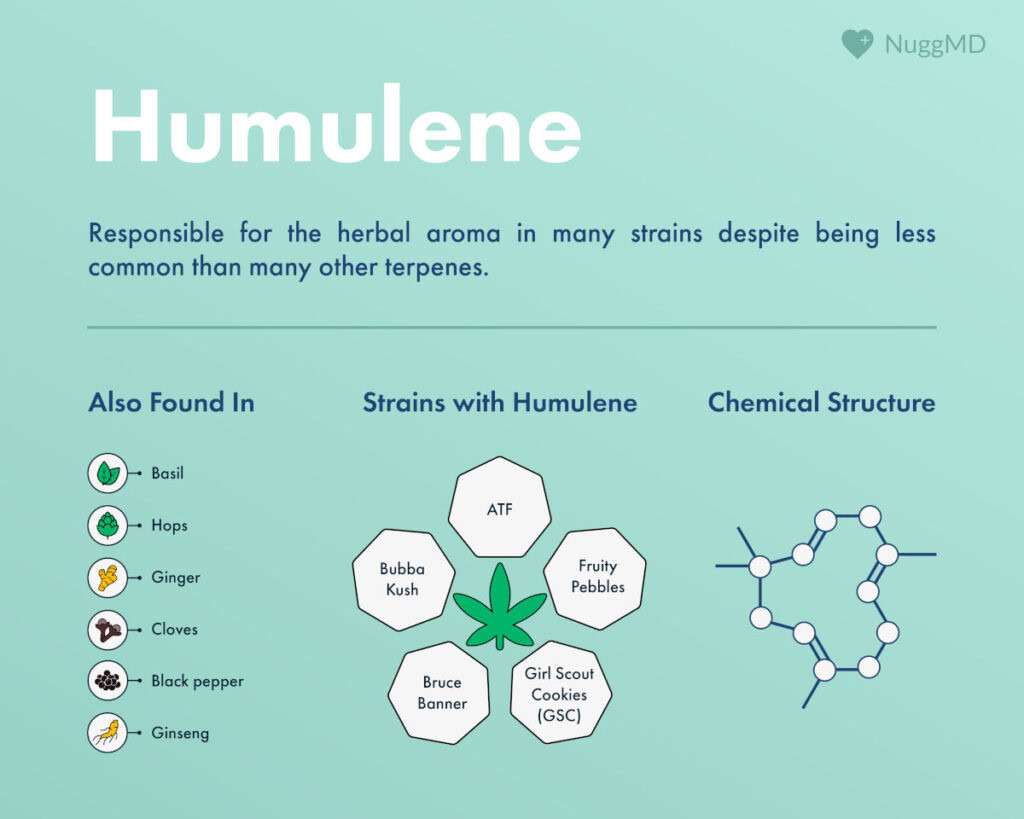
- The terpene humulene features an earthy, woody, and hoppy aroma.
- Humulene has anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects recognized for centuries in Eastern medicine and used in medicines today.
- This terpene is common not only in cannabis but also in hops, sage, and ginseng.
There’s more to cannabis than just CBD and THC. Terpenes influence the scent and flavor of cannabis but also its effects on the body and mind. Humulene is a common terpene with an earthy smell and unique benefits.
What is Humulene?
Terpenes are organic compounds that give plants distinct scents, flavors, and some therapeutic properties. More than 20,000 terpenes exist in nature, many of which are found in the cannabis plant.
The humulene terpene, sometimes called α-humulene, is found in various plants and is especially abundant in hops (Humulus lupulus), a main ingredient in beer.1
Unlike some other terpenes, such as β-caryophyllene, humulene does not bind to cannabinoid receptors directly. Instead, it passes through various molecular pathways, providing anti-inflammatory, pain-reducing, and gastroprotective benefits. This multi-targeted approach, known as polypharmacology, may enhance its therapeutic benefits.2
Humulene is best known for its delicate and unique aroma. Anyone who has caught a whiff of aromatic hops knows its distinct scent. It’s a mix of earthy notes, a touch of citrus, and a hint of spice. Although humulene isn’t as strong-smelling as some of the more dominant terpenes in cannabis, it still adds depth with its unique, subtle scent. Some users also report that humulene can impart a mild, herbal flavor to cannabis, layering the taste profile of various strains.
Effects of the Humulene Terpene
Medicine has relied on humulene and other terpenes for centuries. Research into humulene’s properties supports its multiple benefits. While much of the excitement is based on preclinical studies, the following benefits are among those most frequently cited:
- Anti-inflammatory: Humulene is a potent anti-inflammatory agent. Studies have shown that it can rival traditional anti-inflammatory drugs in reducing inflammation. It may pose as a natural alternative for relief from inflammatory conditions.
- Analgesic (Pain Relief): Humulene has demonstrated notable analgesic properties when applied topically, ingested, or inhaled. This makes it useful in strains that relieve chronic pain.
- Gastroprotective: Research suggests that humulene may help protect the gastrointestinal tract, improving digestive discomforts and function.
- Antimicrobial: Beyond its pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory capabilities, humulene exhibits antibacterial, antifungal, and antiparasitic properties, broadening its potential as a natural remedy.1
These humulene terpene effects may contribute to cannabis's overall efficacy, particularly when combined with other cannabinoids and terpenes in what is known as the entourage effect. This synergy can enhance therapeutic outcomes and improve the overall user experience.
What Other Plants Contain Humulene?

Humulene isn’t exclusive to cannabis. Several other plants contain this valuable terpene, contributing to their unique aromas and therapeutic profiles. Here are a few notable examples:
- Hops (Humulus lupulus): Hops are best known for their role in brewing beer. They naturally contain high levels of humulene, a terpene that contributes to their characteristic aroma. Brewers and botanists value this flavor profile.
- Sage: Commonly used in both culinary and medicinal contexts, sage contains humulene, which adds an earthy and slightly spicy aroma.
- Ginseng: Known for its restorative properties, the ginseng in humulene adds a subtle, aromatic layer to its complex profile.
- Aframomum melegueta: This West African spice, sometimes called “grains of paradise,” is another natural source of humulene. Like black pepper, another humulene-rich spice, its use in cooking and medicine underscores the terpene’s broad-reaching potential.2
Can the Humulene Terpene Help With Common Conditions?
Humulene’s broad and versatile effects have sparked interest among researchers, particularly its potential role in therapeutic and medical applications. While more research is needed, early findings suggest that humulene may help with the following conditions:
- Inflammatory Disorders: Humulene exhibits strong anti-inflammatory properties, which may help it manage chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). By interacting with the body’s immune response, humulene could help reduce swelling, pain, and discomfort associated with long-term inflammation. Early tests in lab-controlled settings show humulene may have applications in treating specific inflammatory cancer cell growth.1
- Pain Management: As a natural analgesic, humulene may provide pain relief in conjunction with cannabinoids like CBD and THC. This could make it beneficial for individuals dealing with chronic pain conditions, migraines, or muscle soreness, potentially reducing discomfort without the need for high doses of THC.
- Digestive Issues: Preliminary research suggests that humulene may have gastroprotective effects, which could help protect the stomach lining and support digestive health. This could be particularly helpful for individuals with acid reflux, ulcers, or general gastrointestinal discomfort, though further studies are needed to confirm these benefits.
- Infectious Diseases: Humulene has demonstrated antimicrobial and antibacterial properties, which could help it fight bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections. Some studies suggest that it may help combat drug-resistant bacteria, offering potential antibiotic-supportive benefits in the future.
Anecdotal reports from cannabis users cite improved overall comfort and a reduction in discomfort associated with inflammation and pain when using strains high in humulene. More clinical studies are necessary to understand and confirm these benefits fully.
Best Strains for Humulene

For those interested in experiencing the benefits of humulene firsthand, several cannabis strains are known for their elevated levels of this terpene. Here are five top strains and a brief overview of their profiles and reported benefits.
Girl Scout Cookies (GSC)
This popular hybrid strain has a sweet, minty, and earthy aroma. Its terpene profile includes humulene and high levels of caryophyllene and limonene. Many GSC varieties tend to promote euphoria and relaxation, ideal for stress relief and mood enhancement.
Bubba Kush
An indica-dominant strain, Bubba Kush exudes rich coffee and chocolate aromas complemented by herby undertones. Its terpene profile includes caryophyllene, limonene, and myrcene, with humulene contributing to its complex scent. Consumers often experience deep relaxation and tranquility, which may aid in alleviating stress and promoting restful sleep.
Bruce Banner
This sativa-leaning hybrid offers a blend of earthy, sweet, and grassy aromas. Its terpene composition features limonene, myrcene, caryophyllene, linalool, and pinene. While humulene is not a primary terpene, it adds depth to the overall profile. Users typically report enhanced creativity, energy, and euphoria, making it suitable for stress relief.
Alaskan Thunder Fuck (ATF)
A sativa-dominant strain, Alaskan Thunder Fuck (ATF) is known for its energizing and uplifting effects. Its terpene composition includes limonene, myrcene, and caryophyllene, with subtle notes of humulene that add to its slightly earthy and spicy undertones. Users may experience an intense cerebral high, enhanced focus, and a boost in creativity. Medicinally, it may help alleviate fatigue, stress, depression, and mild pain.
Fruity Pebbles OG (FPOG)
A hybrid strain with balanced indica and sativa effects, Fruity Pebbles OG (FPOG) has a breakfast cereal scent with sweet, berry-like aroma and tropical citrus flavors. FPOG includes caryophyllene, limonene, and myrcene, with humulene rounding out its earthy complexity. Users may report a euphoric and uplifting high followed by a relaxing body buzz, making it suitable for stress relief, mood enhancement, and mild pain management.
Note: Individual experiences with these strains may vary. Consult with a healthcare professional before using cannabis for therapeutic purposes.
References
- Dalavaye N, Nicholas M, Pillai M, Erridge S, Sodergren MH. The Clinical Translation of α-humulene - A Scoping Review. Planta Med. 2024;90(9):664-674. doi:10.1055/a-2307-8183. ↩︎
- Hartsel JA, Eades J, Hickory B, Makriyannis A. Cannabis sativa and Hemp. Nutraceuticals. Published online 2016:735-754. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-802147-7.00053-x ↩︎
The information in this article and any included images or charts are for educational purposes only. This information is neither a substitute for, nor does it replace, professional legal advice or medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about laws, regulations, or your health, you should always consult with an attorney, physician or other licensed professional.